Differential cellular stiffness contributes to tissue elongation on an expanding surface
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição

Role of mechanical input from the extra-embryonic EVL in directing
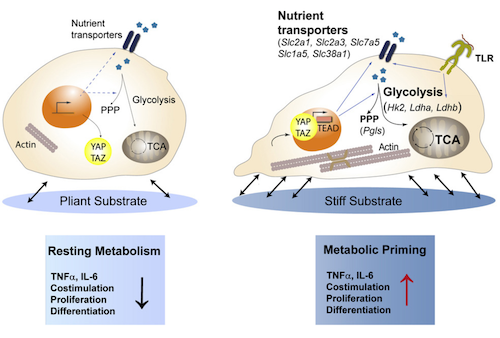
Tissue Stiffness Contributes to Immune Responses & Chronic Aging Diseases
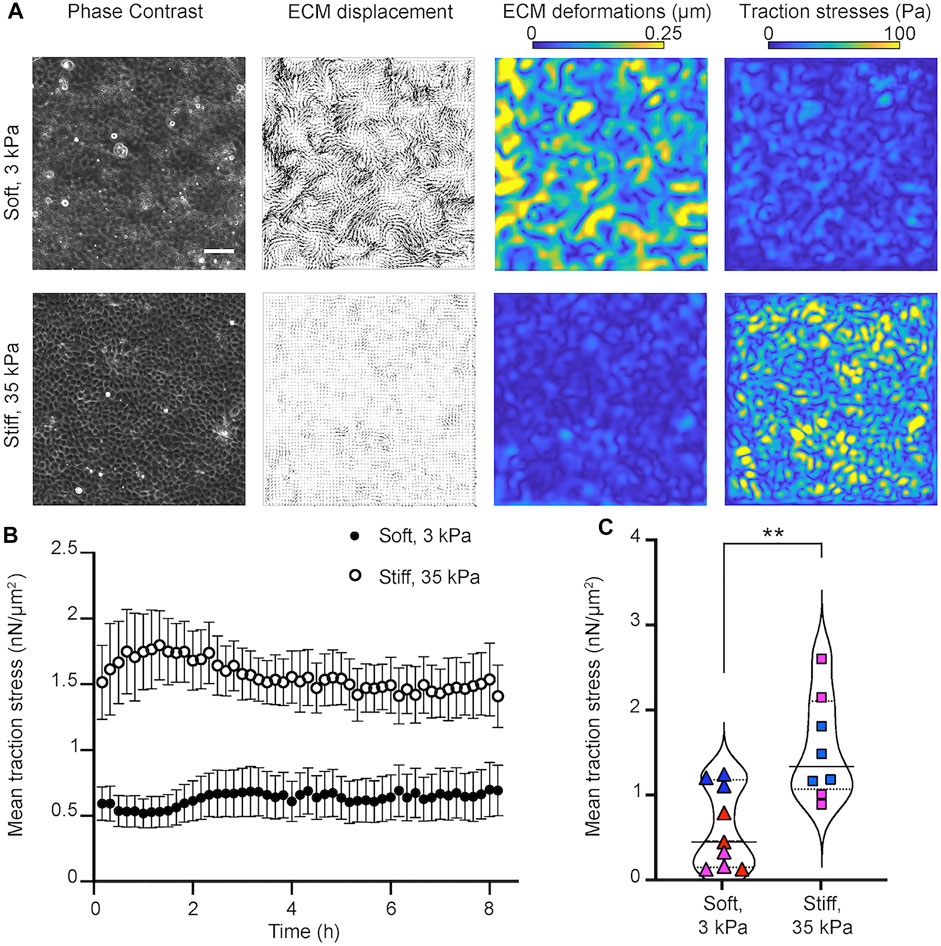
Frontiers A Stiff Extracellular Matrix Favors the Mechanical Cell Competition that Leads to Extrusion of Bacterially-Infected Epithelial Cells

Cell Shape and Durotaxis Explained from Cell-Extracellular Matrix Forces and Focal Adhesion Dynamics - ScienceDirect

Cell elongation and tissue length regulation. A. Epithelial cell

The role of extracellular matrix in biomechanics and its impact on bioengineering of cells and 3D tissues - ScienceDirect
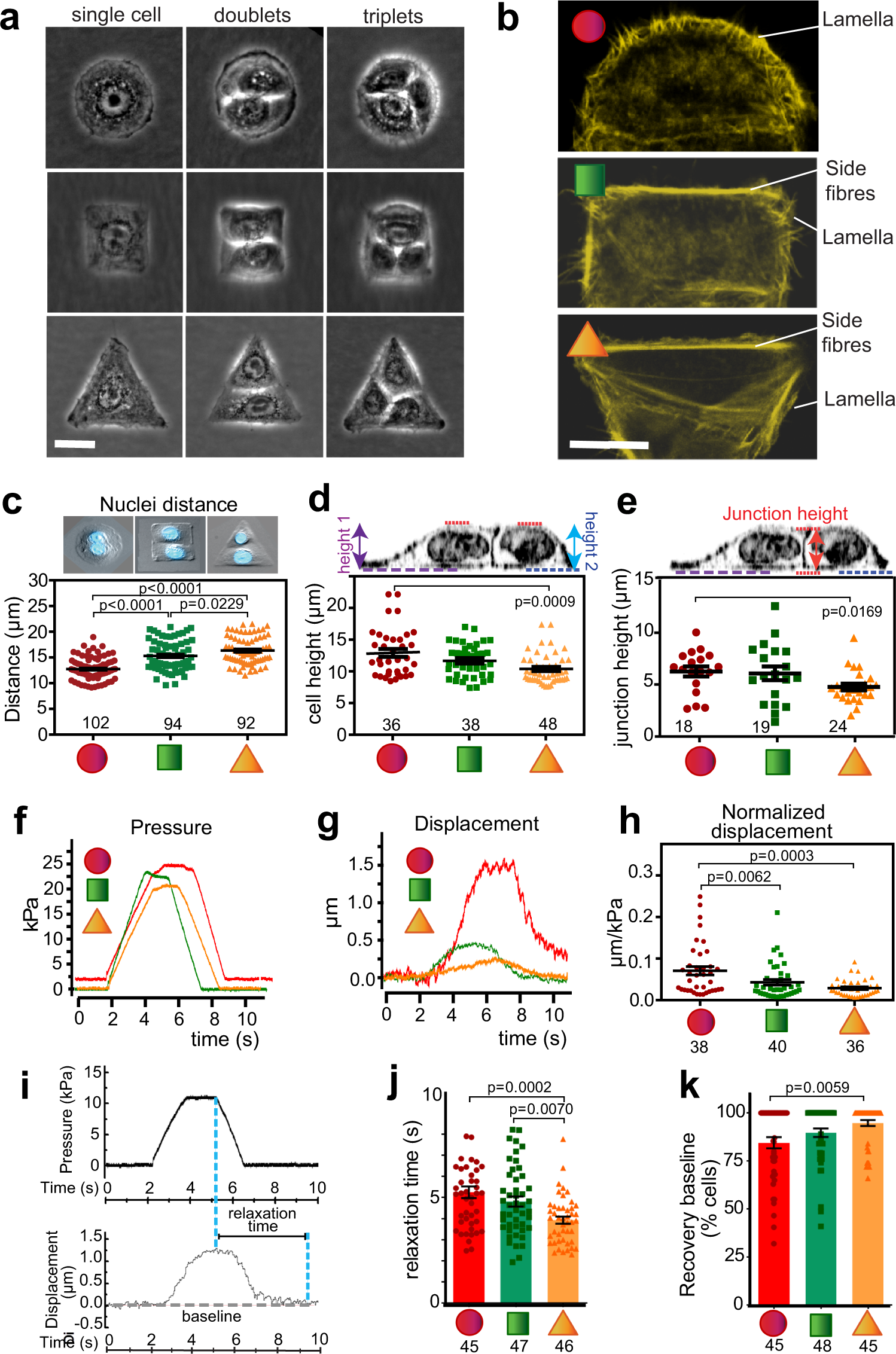
Intrinsic cell rheology drives junction maturation

Strategic outline of interventions targeting extracellular matrix for promoting healthy longevity
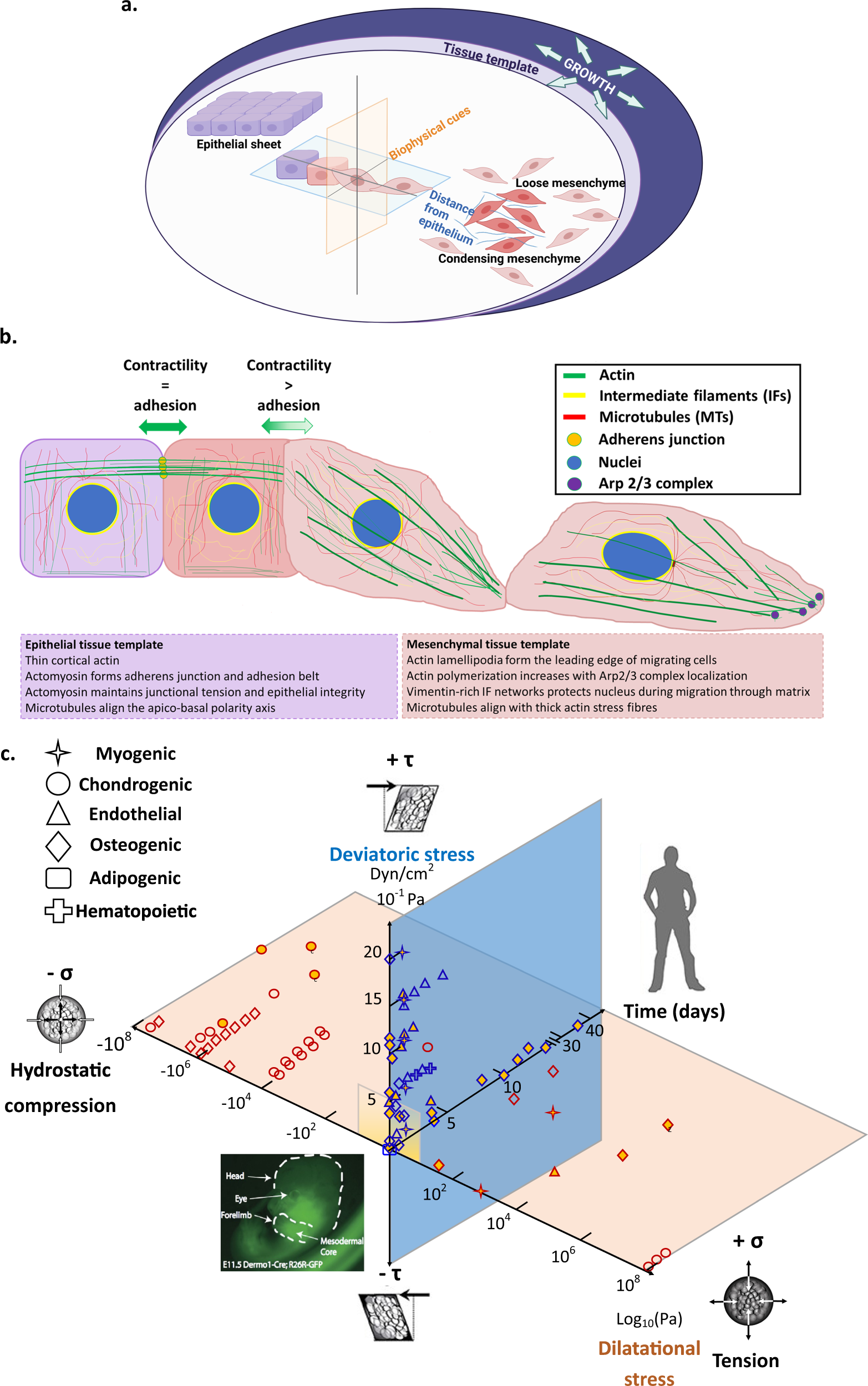
Biomechanical, biophysical and biochemical modulators of cytoskeletal remodelling and emergent stem cell lineage commitment
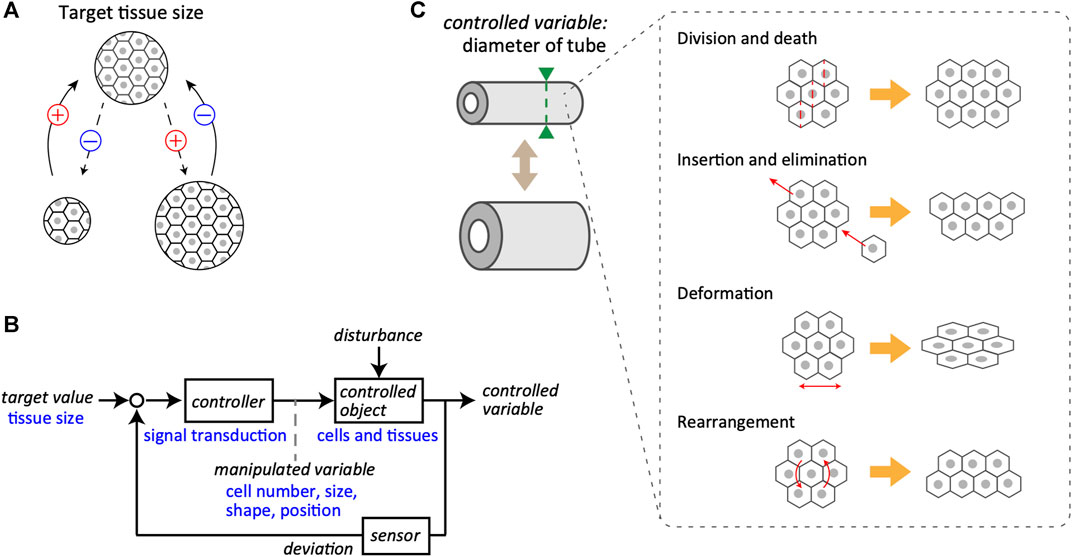
Frontiers Mechanical Feedback Control for Multicellular Tissue Size Maintenance: A Minireview

Nanoscale Surface Topography Reduces Focal Adhesions and Cell Stiffness by Enhancing Integrin Endocytosis

Beyond Tissue Stiffness and Bioadhesivity: Advanced Biomaterials to Model Tumor Microenvironments and Drug Resistance: Trends in Cancer
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)