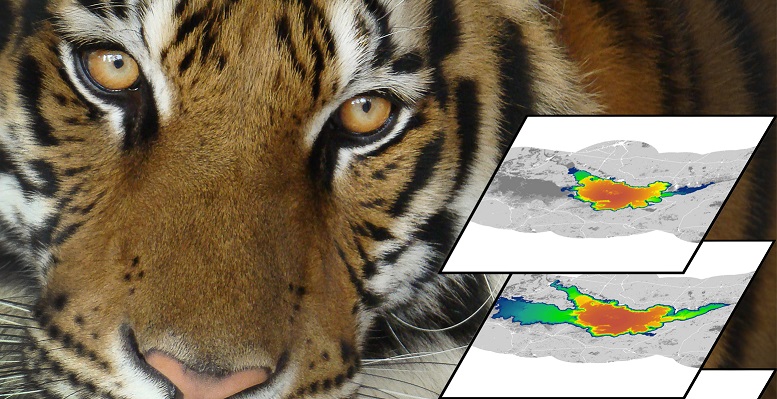
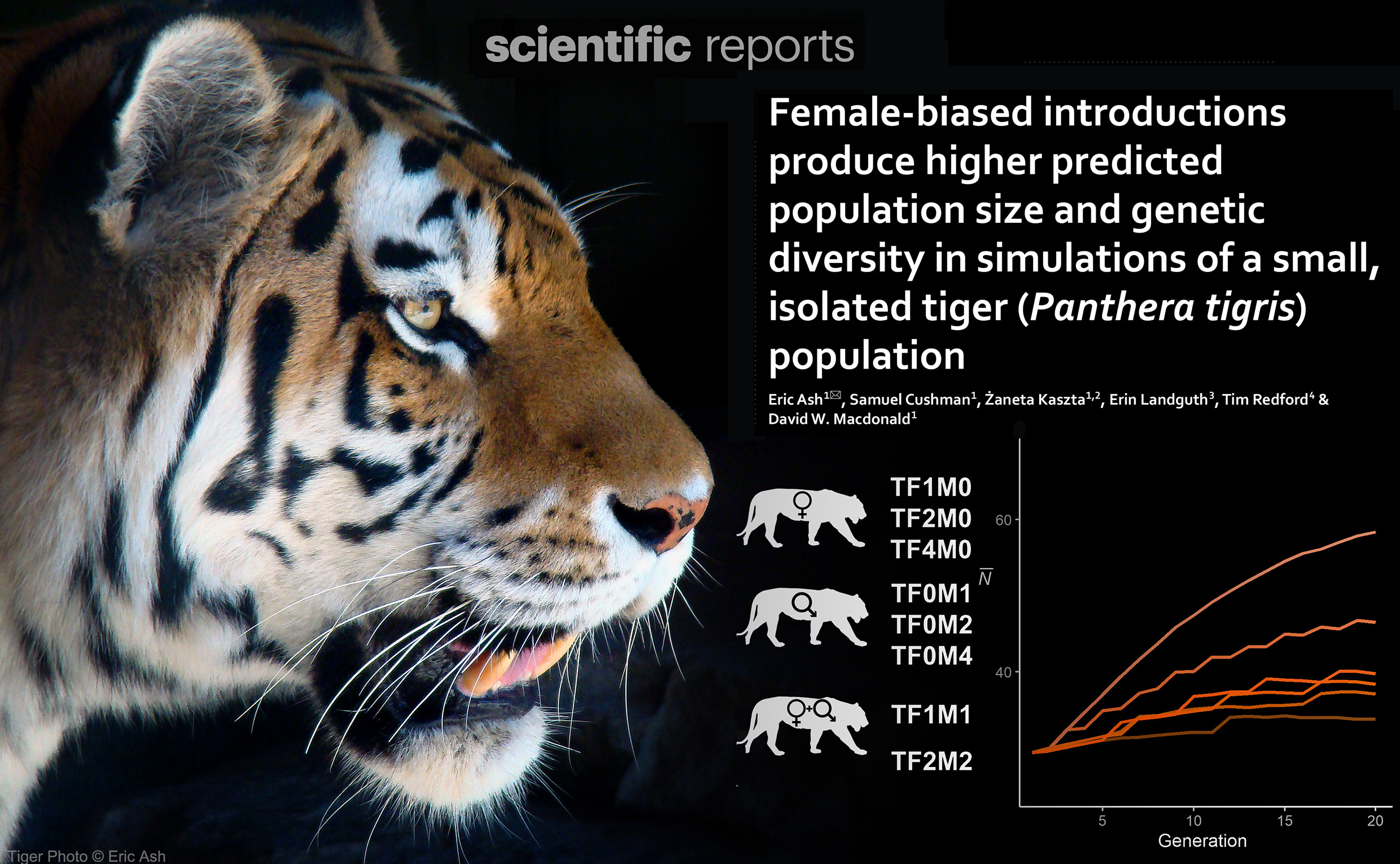
Female-biased introductions produce higher predicted population size and genetic diversity in simulations of a small, isolated tiger (Panthera tigris) population
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
Modelling tiger population numbers and genetic diversity in the

PDF] Landscape Analysis of Adult Florida Panther Habitat

Latest Research - WildCats Conservation Alliance

Demographic Stochasticity and Social Mating System in the Process
Sustainability, Free Full-Text
Frontiers Age-Dependent Dispersal and Relatedness in Tiger

PDF) Comparative genetic analysis of reproductive parameters

Biology Chapter Notes, PDF, Ion

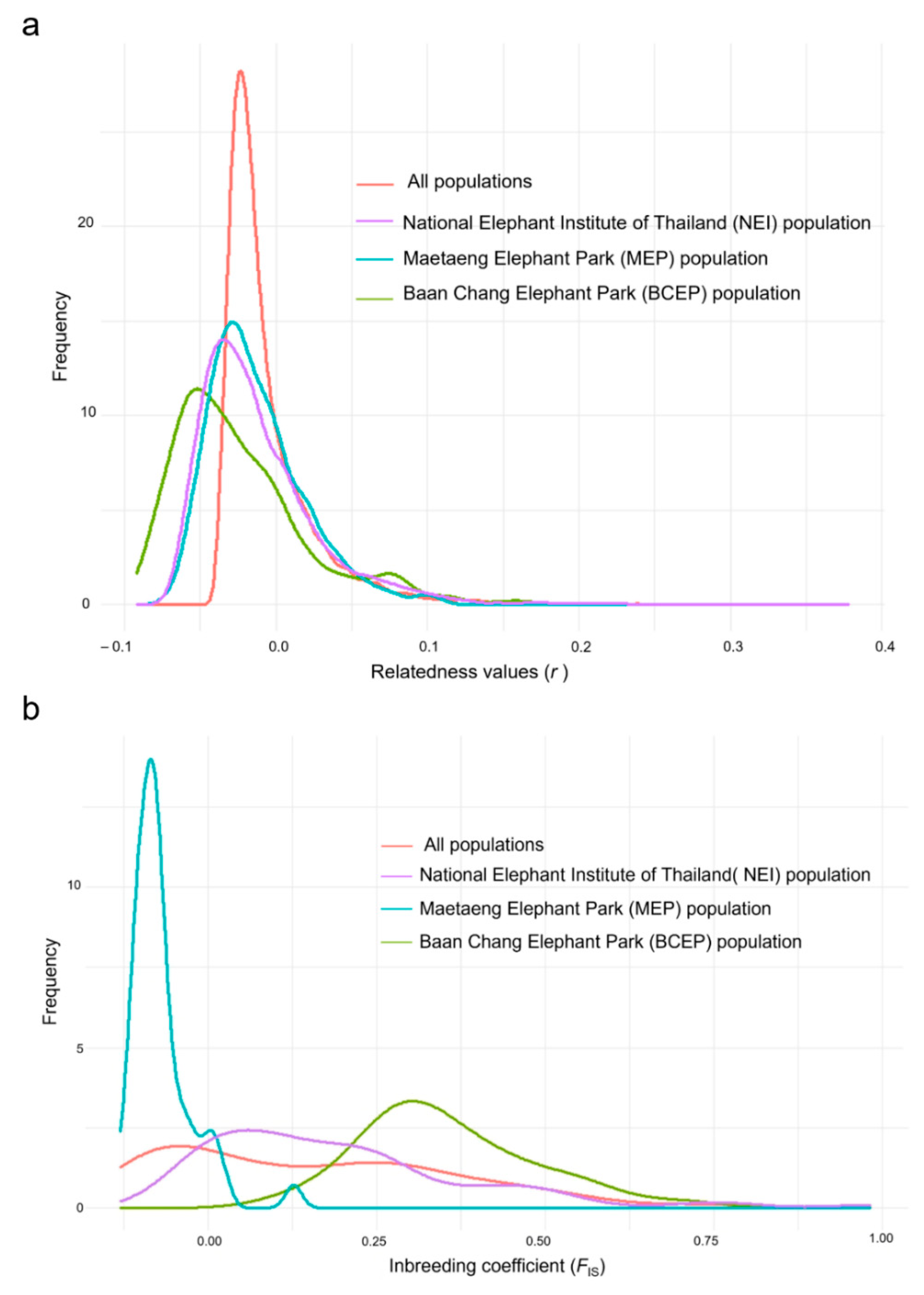
Assessment of population genetic diversity and genetic structure

How methodological changes have influenced our understanding of
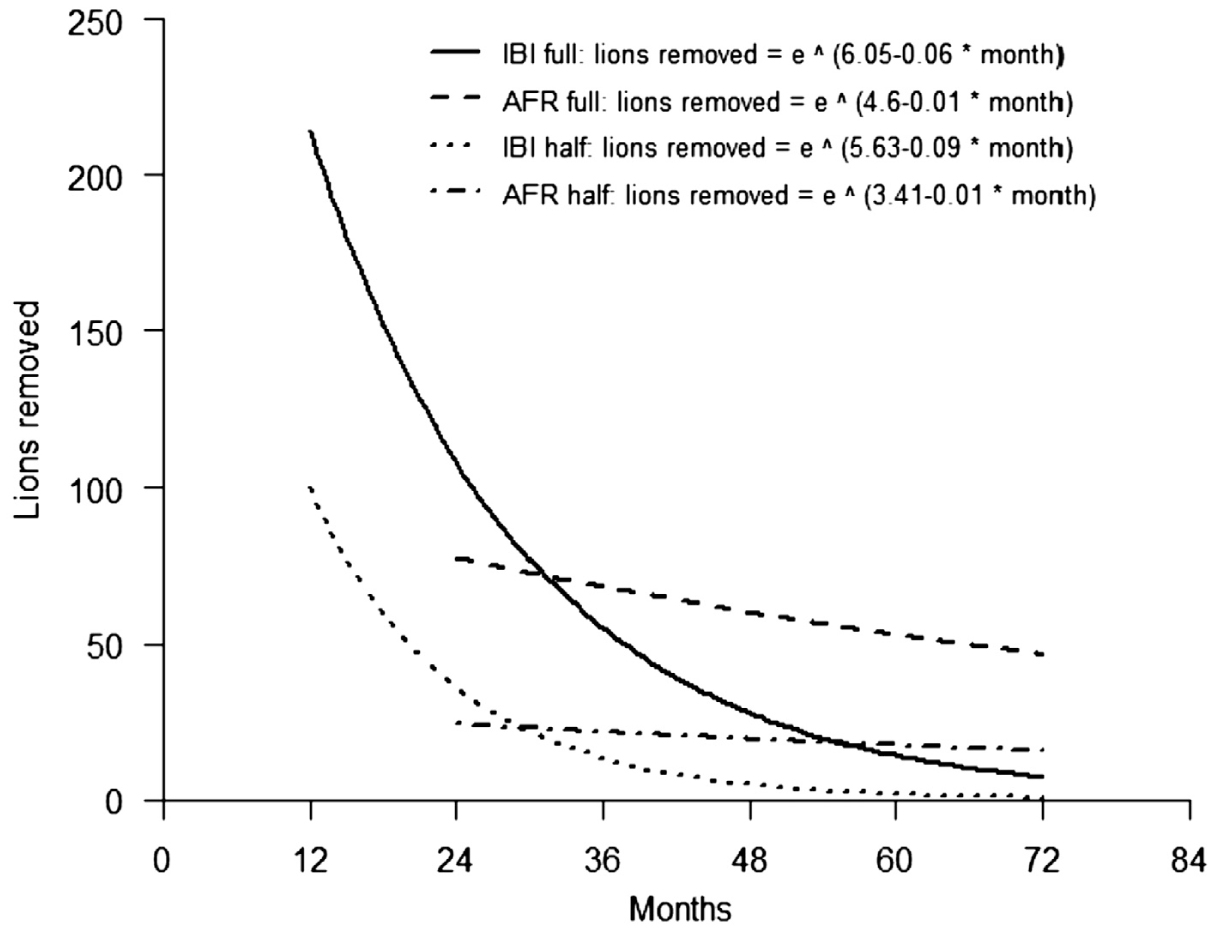
GrowLS: Lion (Panthera leo) Population Growth Simulation for Small
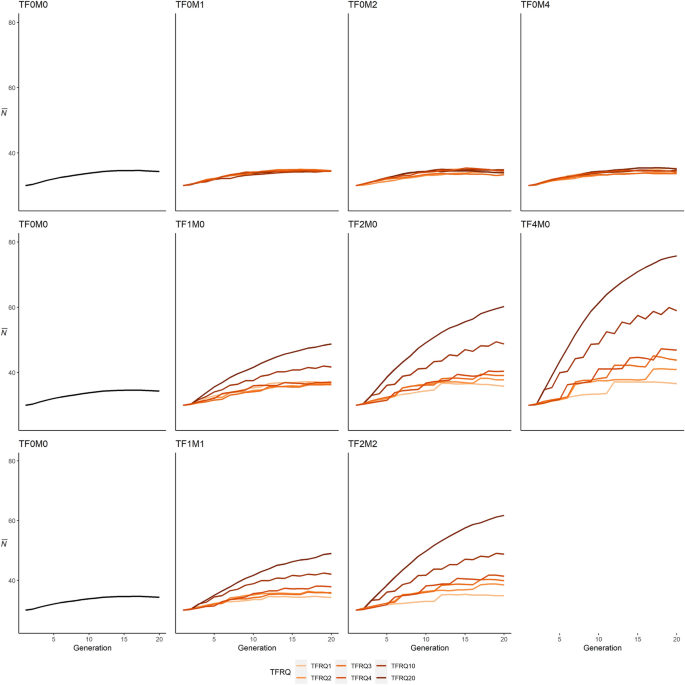
Female-biased introductions produce higher predicted population
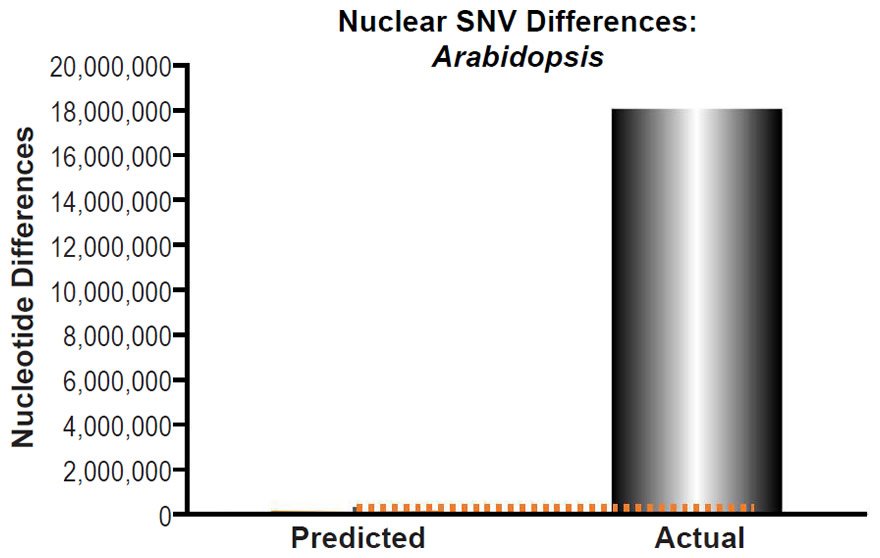
Origin Eukaryotic Genotypic Phenotypic Diversity

Eric Ash Department of Biology

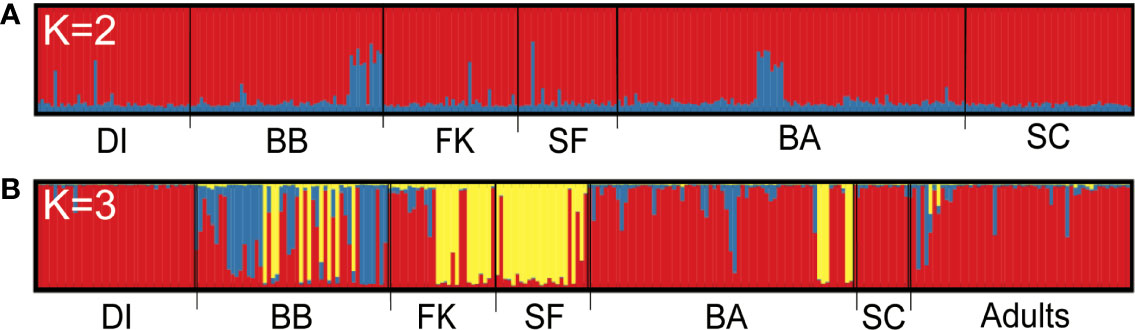
Fine-scale population structure and sex-biased dispersal in
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)