Warming and overfishing could switch the role of fishes in the marine carbon cycle
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
Bony fish are more often recognized as food sources than as carbon regulators. They provide an array of services relevant to climate change mitigation. For instance, they store carbon within their bodies as they grow and export it to deep seas through their sinking feces and carcasses. But they also make carbonates from marine salts within their guts and excrete them at high rates. This makes them especially important within the inorganic carbon cycle of the oceans.

Carbon footprint, economic benefits and sustainable fishing: Lessons for the future from the Western Mediterranean - ScienceDirect
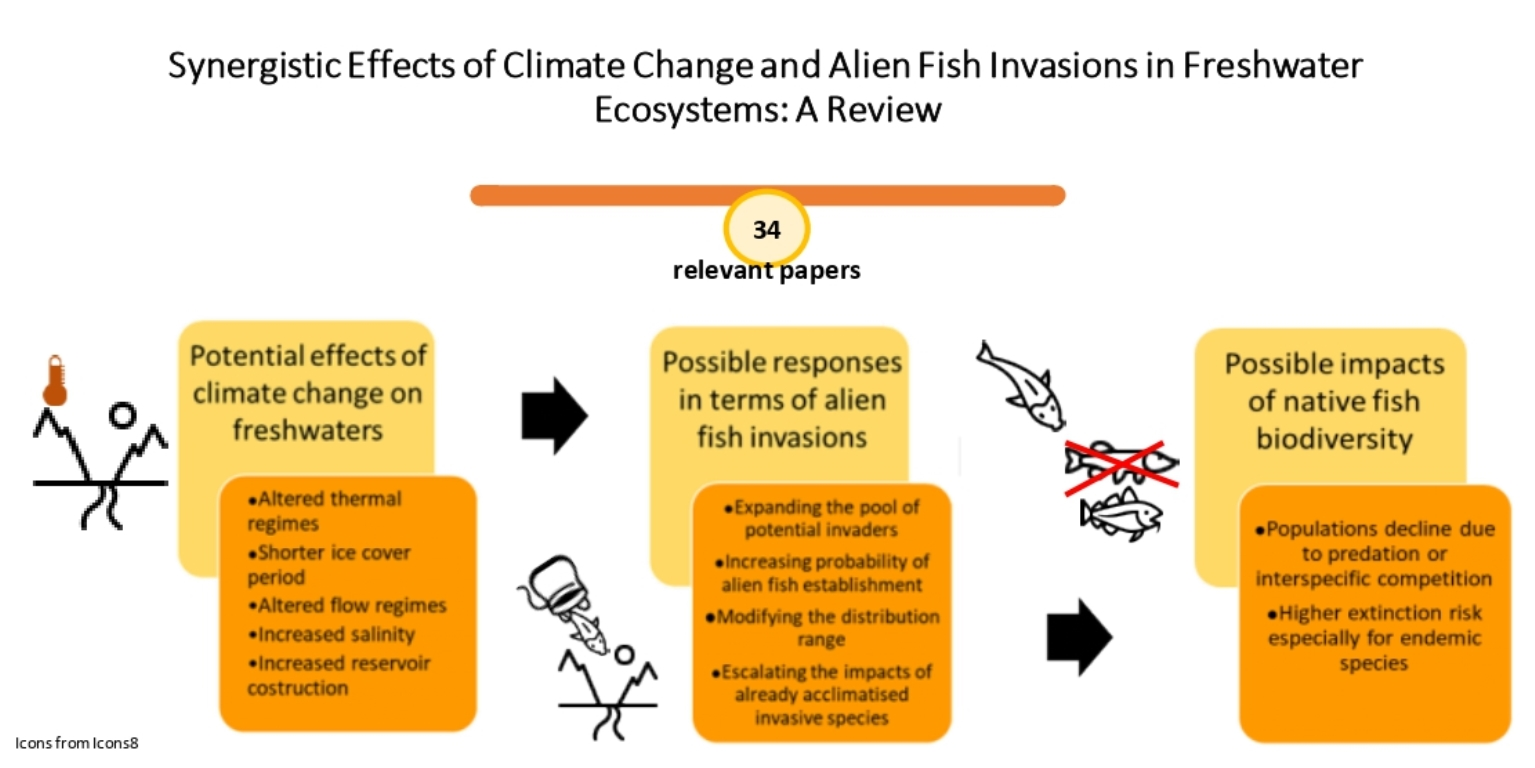
Fishes, Free Full-Text

How will climate change impact fisheries?
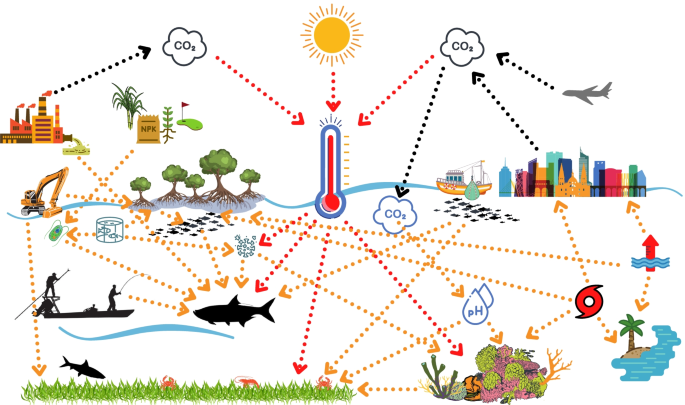
Cascading effects of climate change on recreational marine flats fishes and fisheries

Global Change Biology, Environmental Change Journal

Potential role of seaweeds in climate change mitigation - ScienceDirect

Q&A: How might fishing be impacting the carbon cycle?, Imperial News

PDF] Marine reserves can mitigate and promote adaptation to climate change

Climate change could make fish shrink by up to 30%

Impact of warming on aquatic body sizes explained by metabolic scaling from microbes to macrofauna
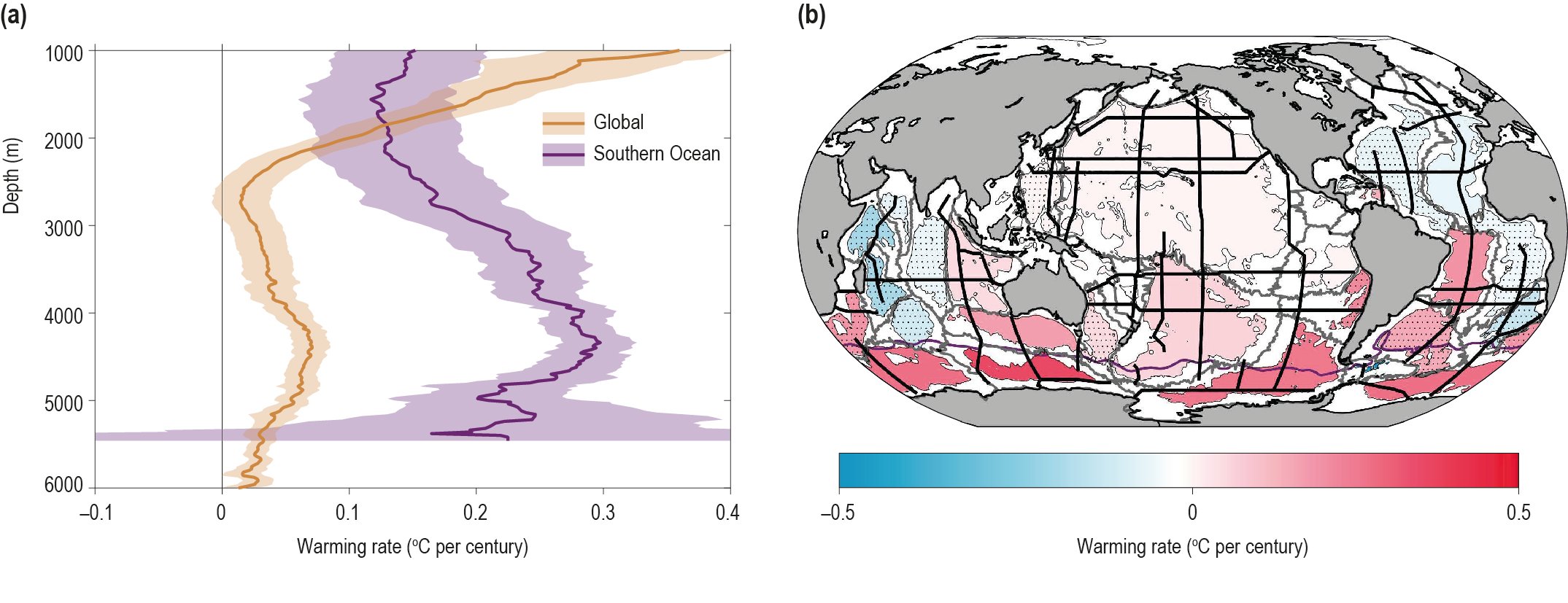
Chapter 5: Changing Ocean, Marine Ecosystems, and Dependent Communities — Special Report on the Ocean and Cryosphere in a Changing Climate

Cold fish: the global cooling effect of ocean life
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)