Rac1 Regulates Neuronal Polarization through the WAVE Complex
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
Neuronal migration and axon growth, key events during neuronal development, require distinct changes in the cytoskeleton. Although many molecular regulators of polarity have been identified and characterized, relatively little is known about their physiological role in this process. To study the physiological function of Rac1 in neuronal development, we have generated a conditional knock-out mouse, in which Rac1 is ablated in the whole brain. Rac1 -deficient cerebellar granule neurons, which do not express other Rac isoforms, showed impaired neuronal migration and axon formation both in vivo and in vitro . In addition, Rac1 ablation disrupts lamellipodia formation in growth cones. The analysis of Rac1 effectors revealed the absence of the Wiskott–Aldrich syndrome protein (WASP) family verprolin-homologous protein (WAVE) complex from the plasma membrane of knock-out growth cones. Loss of WAVE function inhibited axon growth, whereas overexpression of a membrane-tethered WAVE mutant partially rescued axon growth in Rac1 -knock-out neurons. In addition, pharmacological inhibition of the WAVE complex effector Arp2/3 also reduced axon growth. We propose that Rac1 recruits the WAVE complex to the plasma membrane to enable actin remodeling necessary for axon growth.

Coronin 2B Regulates Neuronal Migration via Rac1-Dependent Multipolar–Bipolar Transition

Extracellular and Intracellular Signaling for Neuronal Polarity
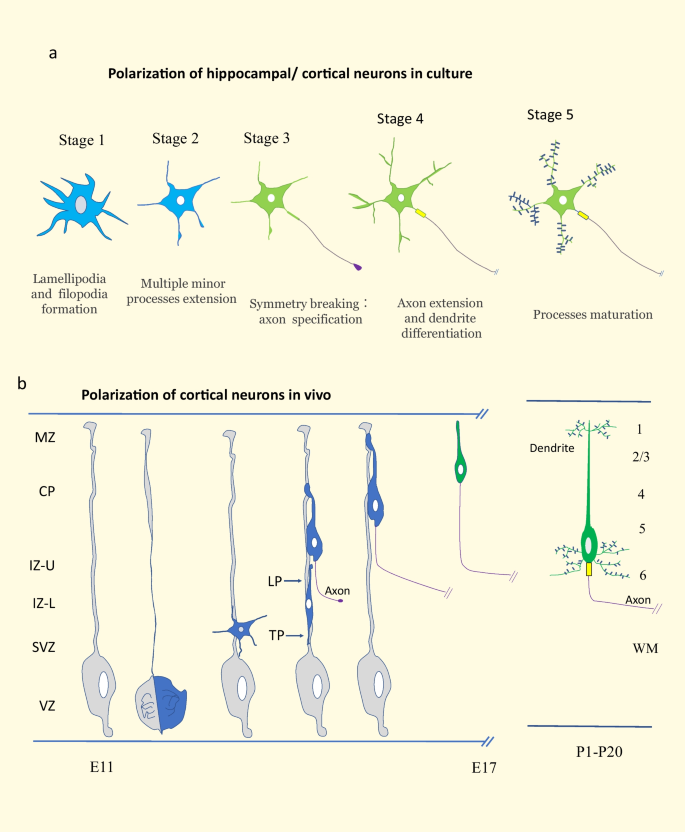
Advances in Understanding the Molecular Mechanisms of Neuronal Polarity
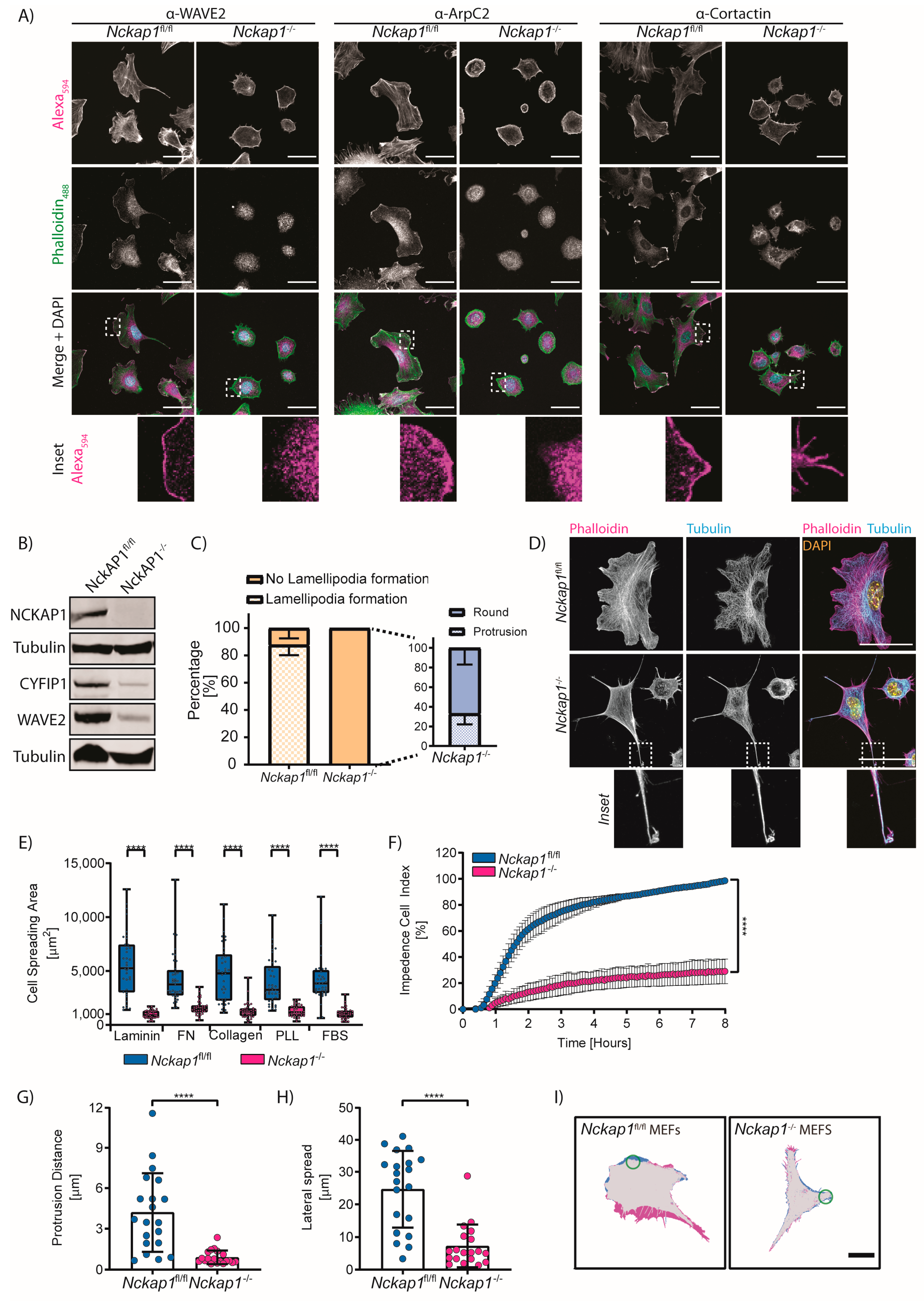
Cells, Free Full-Text
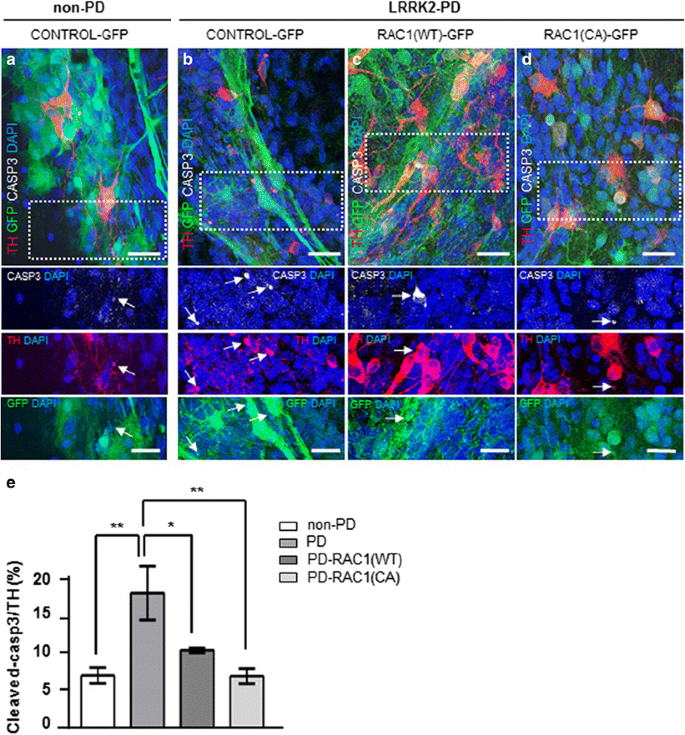
The Small GTPase RAC1/CED-10 Is Essential in Maintaining Dopaminergic Neuron Function and Survival Against α-Synuclein-Induced Toxicity
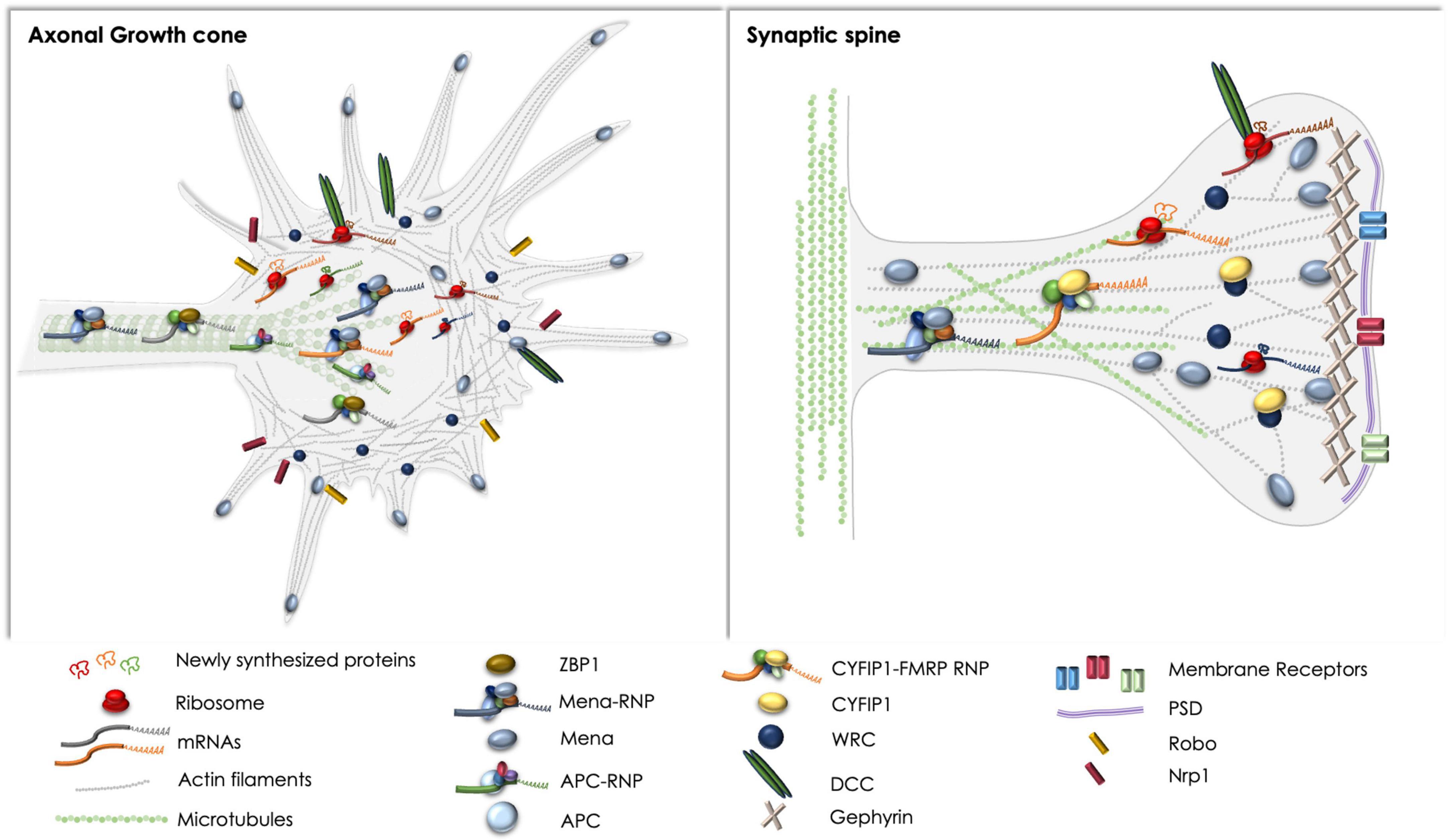
Frontiers Local mRNA translation and cytoskeletal reorganization: Mechanisms that tune neuronal responses

Neuronal actin cytoskeleton gain of function in the human brain - eBioMedicine

Journal of Cellular Physiology, Cell Biology Journal
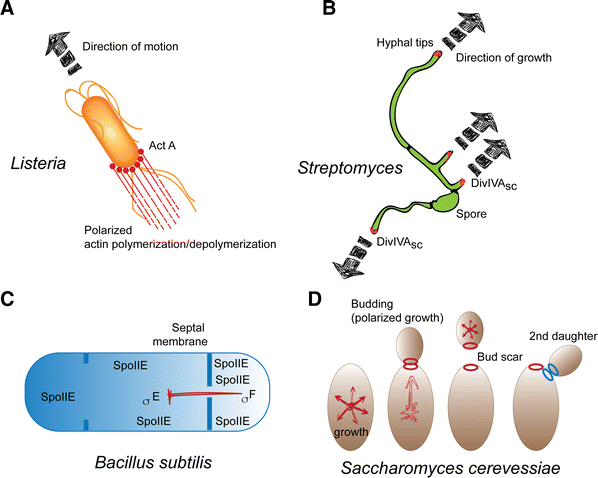
PAR3–PAR6–atypical PKC polarity complex proteins in neuronal polarization
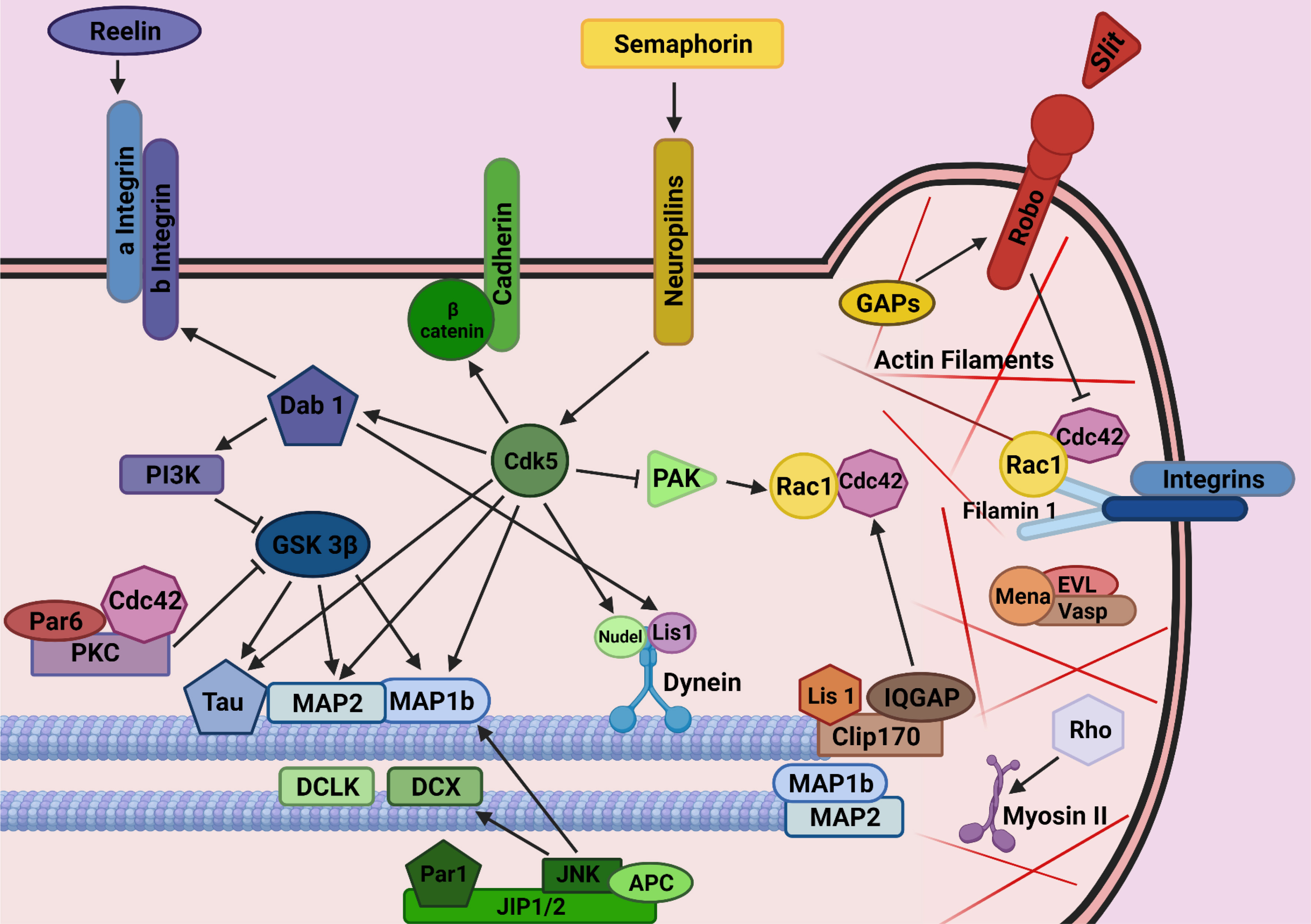
Cortical interneuron development: a role for small Rho GTPases
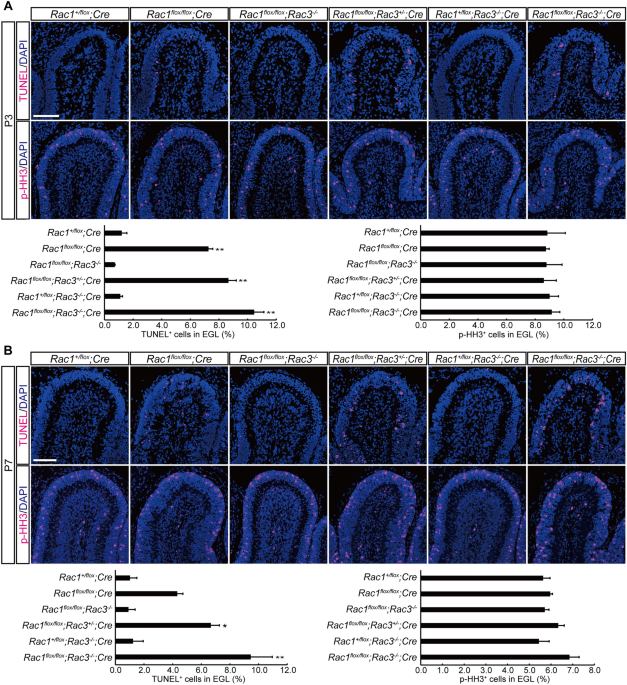
Rac-deficient cerebellar granule neurons die before they migrate to the internal granule layer

Full article: Regulation of cell adhesion and migration in cortical neurons
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)







