Metabolites, Free Full-Text
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
This research focused on establishing a hierarchy concerning the influence of various biological markers and body composition parameters on preventing, diagnosing and managing Metabolic Syndrome (MetS). Our cross-sectional cohort study included 104 subjects without any atherosclerotic antecedent pathology, organized in two groups (with and without MetS). All participants underwent clinical and anthropometric measurements, DEXA investigation and blood tests for all MetS criteria, together with adiponectin, leptin, insulin, uric acid and CRP. Based on mathematical logic, we calculated a normalized sensitivity score to compare the predictive power of biomarkers and parameters associated with MetS, upon the prevalence of MetS. Patients with MetS report higher levels of uric acid (p = 0.02), CRP (p = 0.012) and lower levels of adiponectin (p = 0.025) than patients without MetS. The top three biological markers with the highest predictive power of the prevalence of the disease are HDL, insulin, and adiponectin:leptin ratio, and the top three body composition parameters are trunk fat-free percentage, waist-height ratio and trunk fat percentage. Their high sensitivity scores differentiate them from all the other markers analysed in the study. Our findings report relevant scores for estimating the importance of cardiometabolic risks in the prevalence of MetS. The high rank of protective markers, HDL and trunk fat-free percentage, suggest that positive effects have a stronger association with the prevalence of MetS, than negative ones do. Therefore, this risk stratification study provides important support for prevention and management programs regarding MetS.

Metabolite-induced in vivo fabrication of substrate-free organic bioelectronics
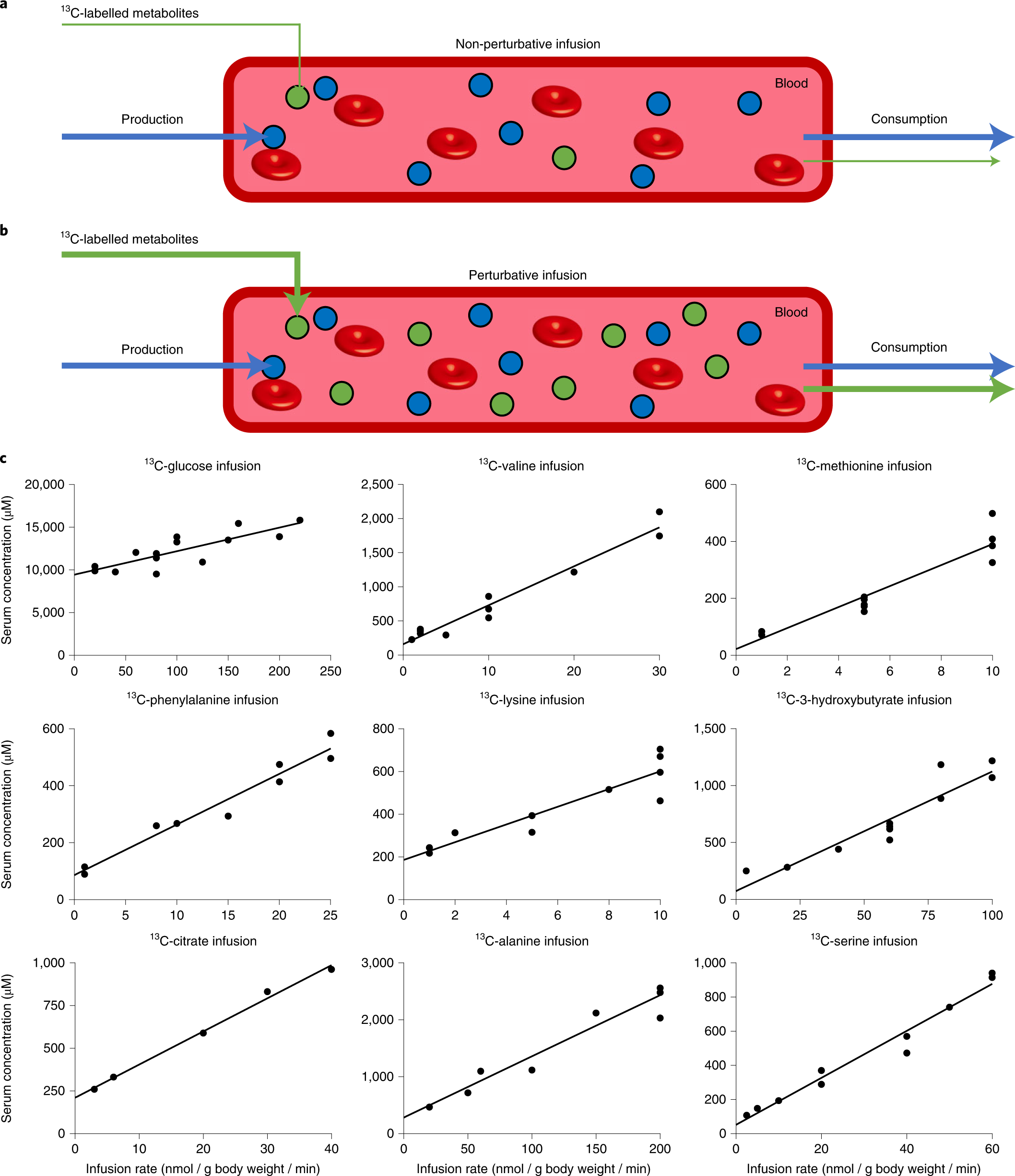
Circulating metabolite homeostasis achieved through mass action

MetNet: Metabolite Network Prediction from High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry Data in R Aiding Metabolite Annotation
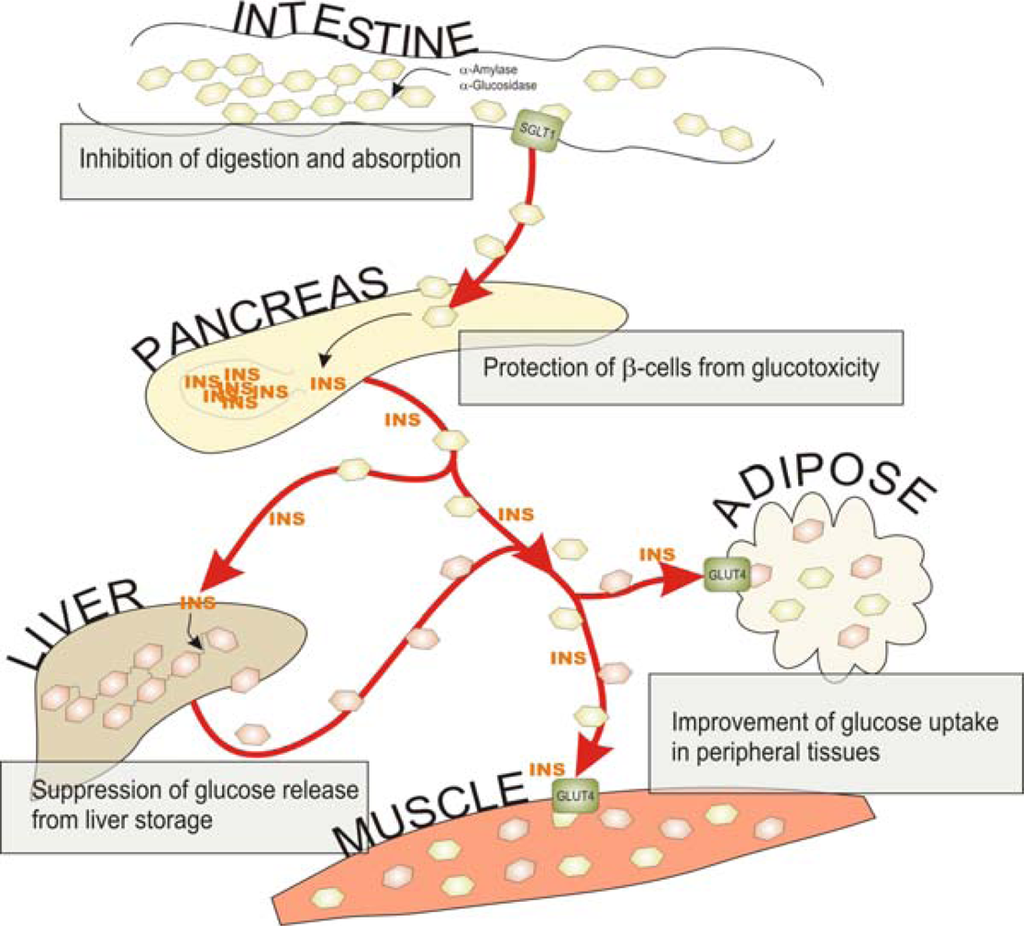
IJMS, Free Full-Text

PDF) Absorption rates and free radical scavenging values of vitamin C-lipid metabolites in human lymphoblastic cells

Lipid metabolism in cancer - Santos - 2012 - The FEBS Journal - Wiley Online Library

Multi-omics-based label-free metabolic flux inference reveals obesity-associated dysregulatory mechanisms in liver glucose metabolism - ScienceDirect
Phagocytes, toxic oxygen metabolites and inflammatory bowel disease: implications for treatment. - Abstract - Europe PMC

Individual variability in human blood metabolites identifies age-related differences

Multi-omics-based label-free metabolic flux inference reveals obesity-associated dysregulatory mechanisms in liver glucose metabolism - ScienceDirect
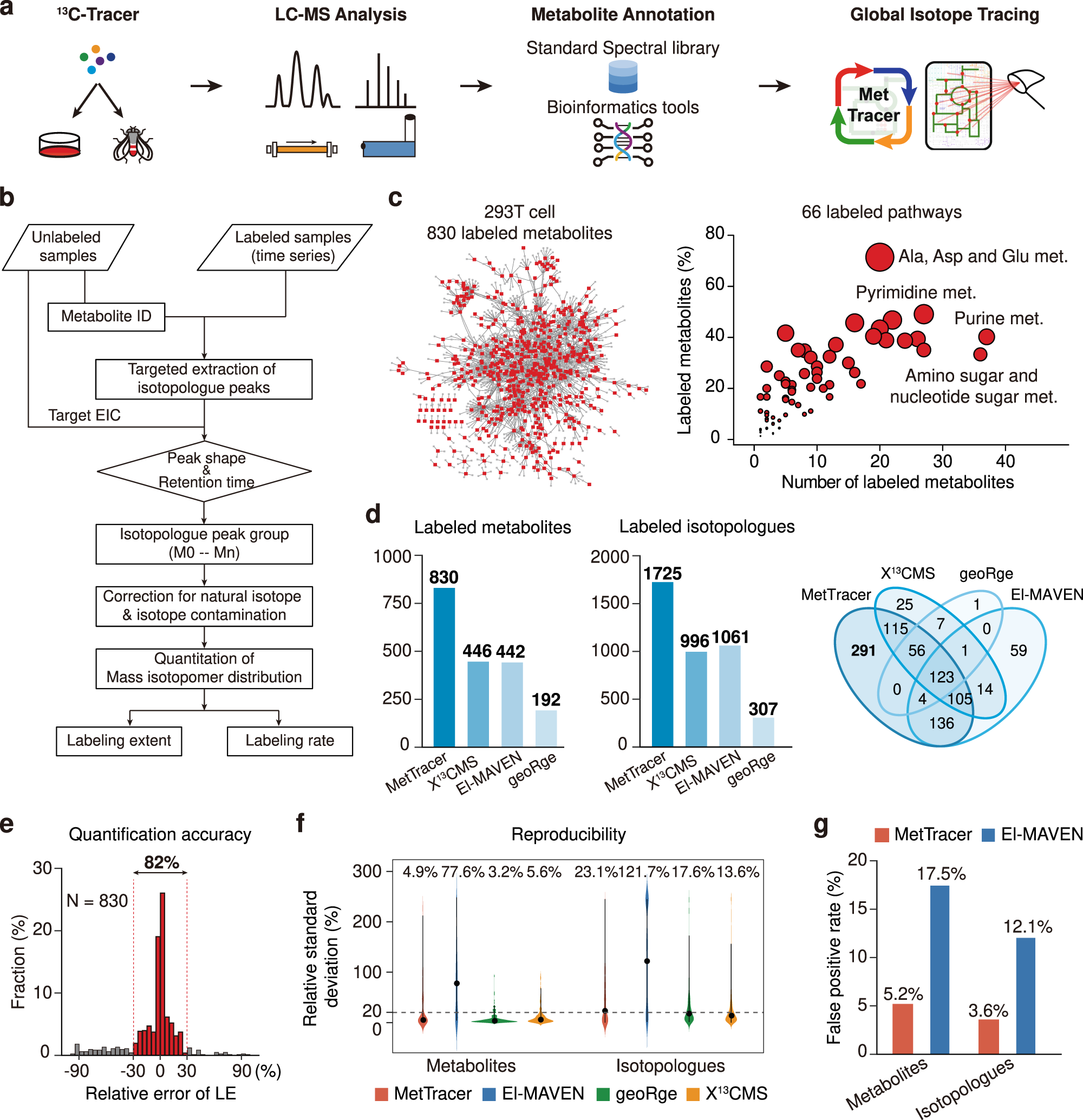
Global stable-isotope tracing metabolomics reveals system-wide metabolic alternations in aging Drosophila

Metabolism - Incomplete Oxidation, Energy Production, Enzymes

A coarse-grained NADH redox model enables inference of subcellular metabolic fluxes from fluorescence lifetime imaging
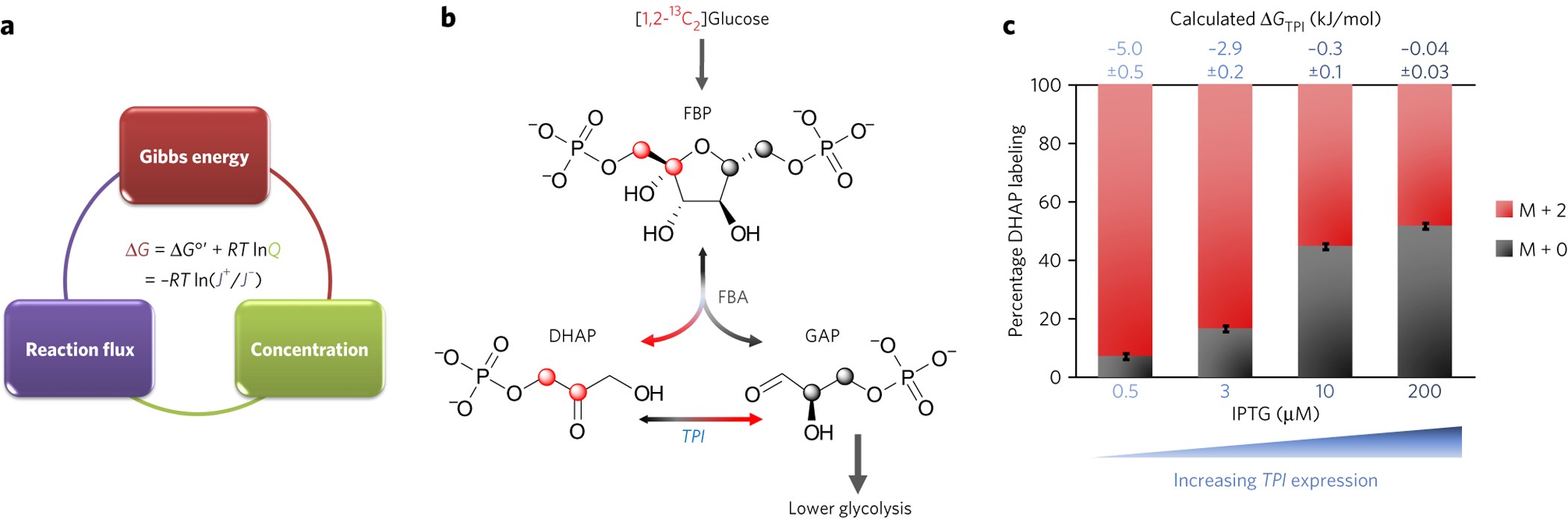
Metabolite concentrations, fluxes and free energies imply efficient enzyme usage
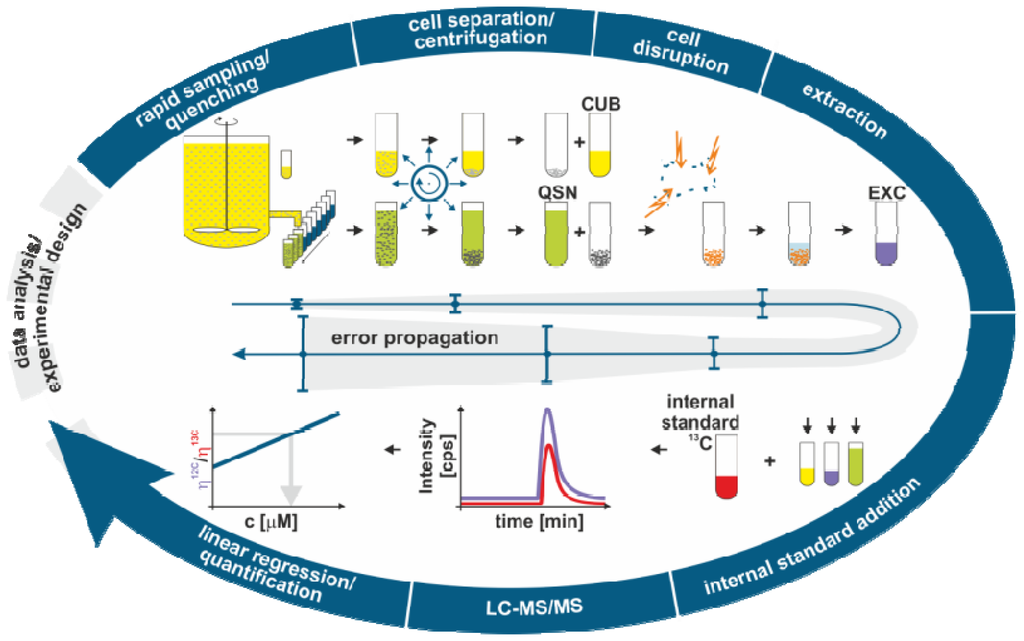
Metabolites, Free Full-Text
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)