Adult Neurogenesis Is Altered by Circadian Phase Shifts and the Duper Mutation in Female Syrian Hamsters
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
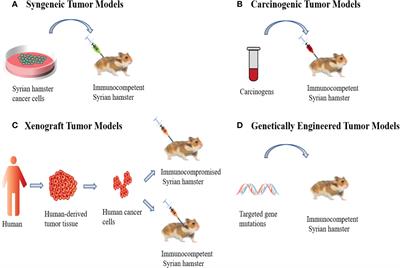
Cell birth and survival in the adult hippocampus are regulated by a circadian clock. Rotating shift work and jet lag disrupt circadian rhythms and aggravate disease. Internal misalignment, a state in which abnormal phase relationships prevail between and within organs, is proposed to account for adverse effects of circadian disruption. This hypothesis has been difficult to test because phase shifts of the entraining cycle inevitably lead to transient desynchrony. Thus, it remains possible that phase shifts, regardless of internal desynchrony, account for adverse effects of circadian disruption and alter neurogenesis and cell fate. To address this question, we examined cell birth and differentiation in the duper Syrian hamster ( Mesocricetus auratus ), a Cry1 -null mutant in which re-entrainment of locomotor rhythms is greatly accelerated. Adult females were subjected to alternating 8 h advances and delays at eight 16 d intervals. BrdU, a cell birth marker, was given midway through the experiment. Repeated phase shifts decreased the number of newborn non-neuronal cells in WT, but not in duper hamsters. The duper mutation increased the number of BrdU-IR cells that stained for NeuN, which marks neuronal differentiation. Immunocytochemical staining for proliferating cell nuclear antigen indicated no overall effect of genotype or repeated shifts on cell division rates after 131 days. Cell differentiation, assessed by doublecortin, was higher in duper hamsters but was not significantly altered by repeated phase shifts. Our results support the internal misalignment hypothesis and indicate that Cry1 regulates cell differentiation. Phase shifts may determine neuronal stem cell survival and time course of differentiation after cell birth. Figure created with BioRender.

Effect of circadian disruption on FST. (A) Total time spent

A) Cavalieri estimates of total hippocampal volume in Bmal1 (+/+

Adult Neurogenesis Is Altered by Circadian Phase Shifts and the

The circadian clock in adult neural stem cell maintenance
accelerated phase shifting of wheel-running activity after an Ld

Actograms (left) and corresponding χ 2 periodograms (right) of

Number of animals (frequency) exhibiting free-running circadian

Immunohistochemistry in the dentate gyrus (DG) of wild-type and

mPer2 mutation increased in vitro neural stem/progenitor cell

Photic Resetting and Entrainment in CLOCK-Deficient Mice - Robert

The duper mutation reveals previously unsuspected functions of

PRC of (A) wt, (B) t ss , (C) super duper, and (D) duper hamsters
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-179244728-5ae768f53037130036e397b4.jpg)

