Insect Infestation Increases Viscosity of Biogenic Secondary Organic Aerosol
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição

Air pollutants degrade floral scents and increase insect foraging times - ScienceDirect

The viscosity of atmospherically relevant organic particles. - Abstract - Europe PMC

Loop Celia Faiola

Viscosity of α-pinene secondary organic material and implications for particle growth and reactivity

A biogenic secondary organic aerosol source of cirrus ice nucleating particles. - Abstract - Europe PMC

Significant secondary organic aerosol production from aqueous-phase processing of two intermediate volatility organic compounds - ScienceDirect

Insect Infestation Increases Viscosity of Biogenic Secondary Organic Aerosol
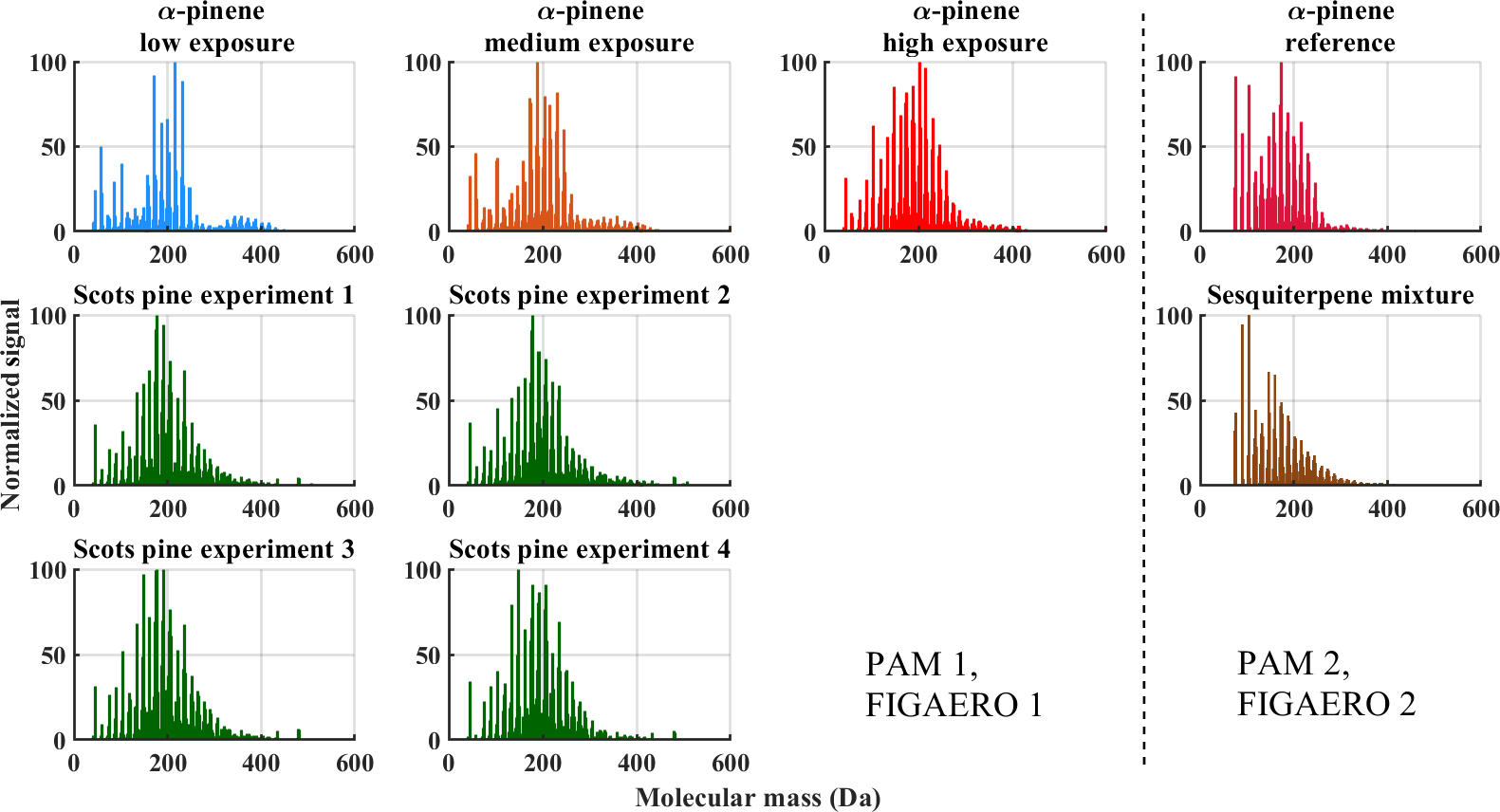
ACP - Composition and volatility of secondary organic aerosol (SOA) formed from oxidation of real tree emissions compared to simplified volatile organic compound (VOC) systems

Morphology and Viscosity Changes after Reactive Uptake of Isoprene Epoxydiols in Submicrometer Phase Separated Particles with Secondary Organic Aerosol Formed from Different Volatile Organic Compounds
Insects October 2020 - Browse Articles
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)







