IJMS, Free Full-Text
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
Induced resistance by elicitors is considered to be an eco-friendly strategy to stimulate plant defense against pathogen attack. In this study, we elucidated the effect of salicylic acid (SA) on induced resistance in rubber tree against Phytophthora palmivora and evaluated the possible defense mechanisms that were involved. For SA pretreatment, rubber tree exhibited a significant reduction in disease severity by 41%. Consistent with the occurrence of induced resistance, the pronounced increase in H2O2 level, catalase (CAT) and peroxidase (POD) activities were observed. For defense reactions, exogenous SA promoted the increases of H2O2, CAT, POD and phenylalanine ammonia lyase (PAL) activities, including lignin, endogenous SA and scopoletin (Scp) contents. However, SA had different effects on the activity of each CAT isoform in the particular rubber tree organs. Besides, three partial cDNAs encoding CAT (HbCAT1, HbCAT2 and HbCAT3) and a partial cDNA encoding PAL (HbPAL) were isolated from rubber tree. Moreover, the expressions of HbCAT1, HbPAL and HbPR1 were induced by SA. Our findings suggested that, upon SA priming, the elevated H2O2, CAT, POD and PAL activities, lignin, endogenous SA and Scp contents, including the up-regulated HbCAT1, HbPAL and HbPR1 expressions could potentiate the resistance in rubber tree against P. palmivora.
IJMS, Free Full-Text
IJMS, Free Full-Text
IJMS, Free Full-Text
IJMS, Free Full-Text
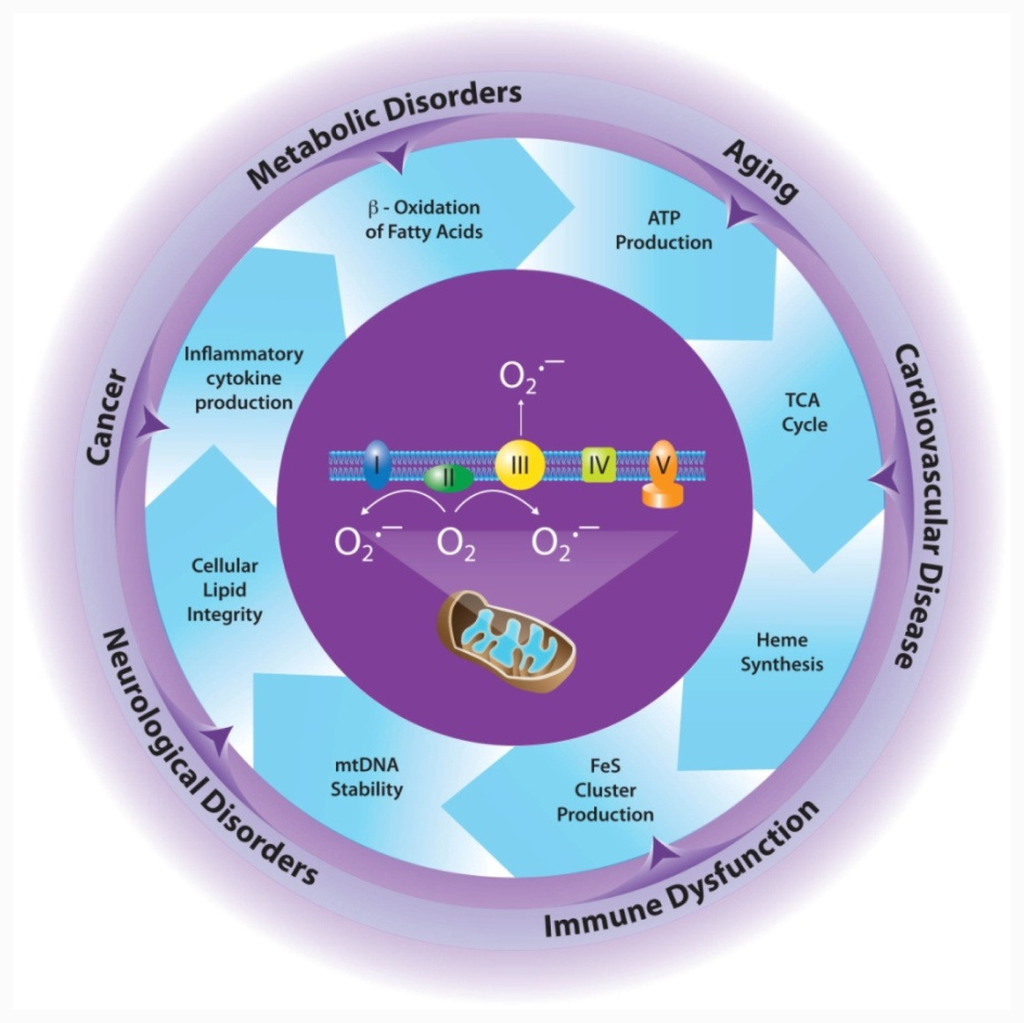
IJMS, Free Full-Text

Cleverativity on LinkedIn: IJMS, Free Full-Text
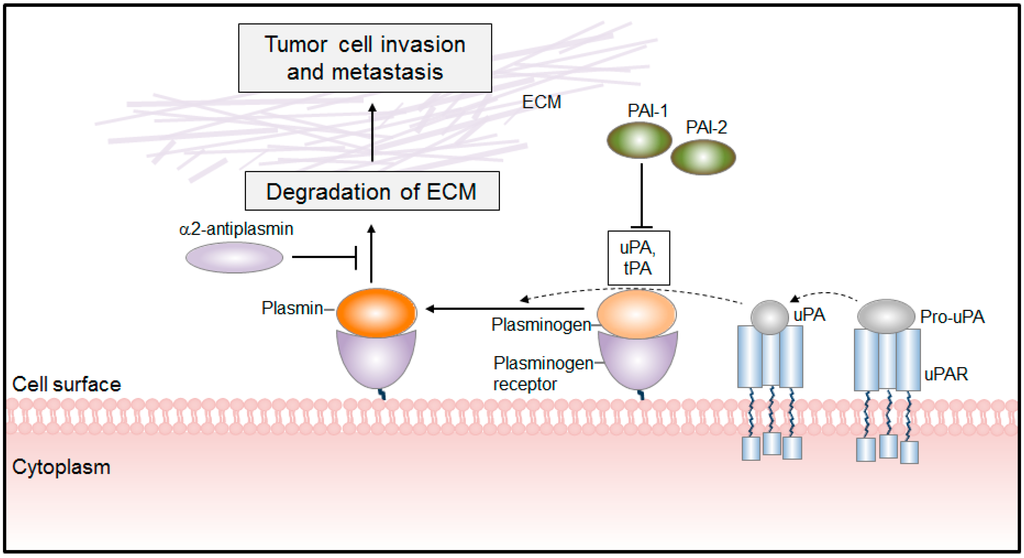
IJMS, Free Full-Text
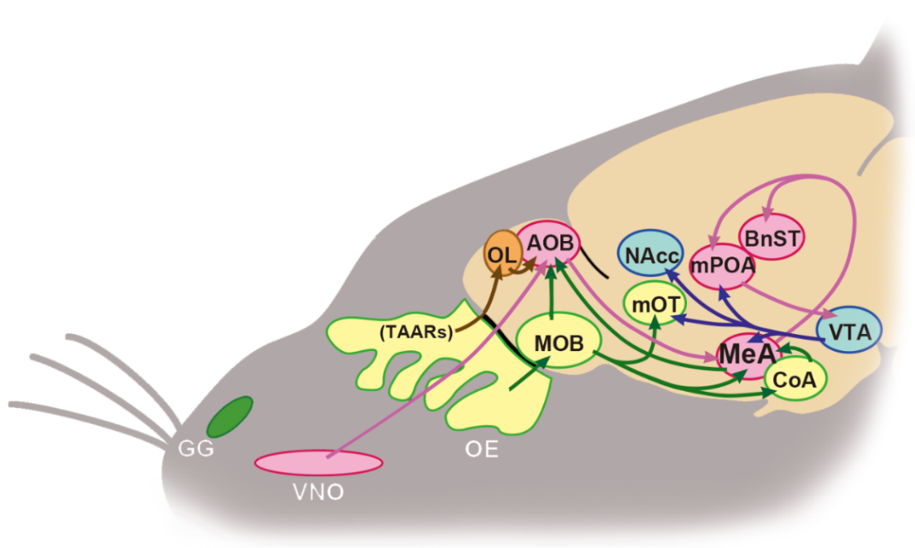
Ijms Free Full Text Neural And Hormonal Basis Of 49680
Ijms Free Full Text Neural And Hormonal Basis Of 49680

IJMS Free Full Text A High Molecular Mass 26650
Ijms Free Full Text Non Invasive Detection Of Extracellular Matrix
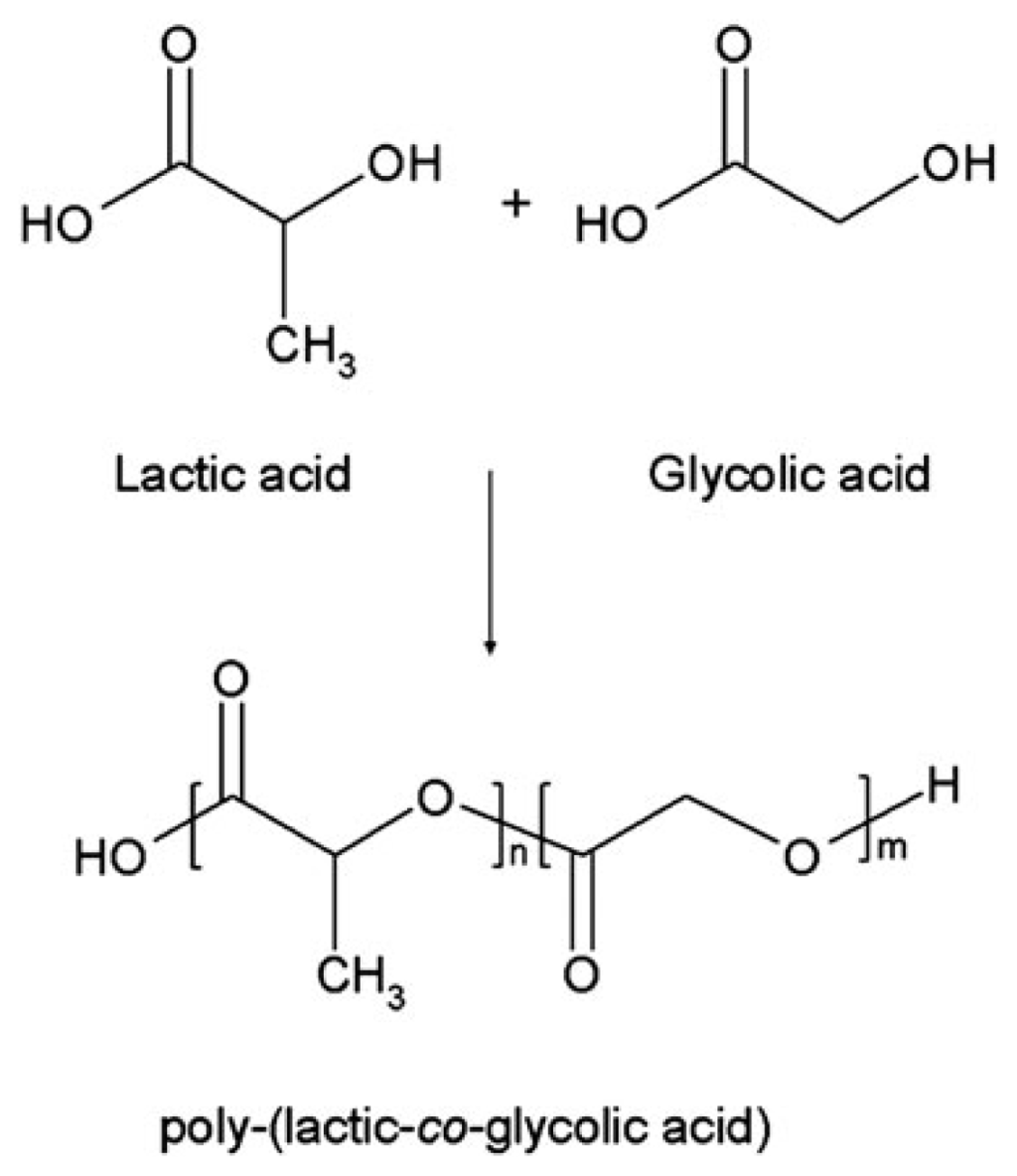
IJMS, Free Full-Text
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)







