Cells, Free Full-Text
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
The genus Aspergillus, one of the most abundant airborne fungi, is classified into hundreds of species that affect humans, animals, and plants. Among these, Aspergillus nidulans, as a key model organism, has been extensively studied to understand the mechanisms governing growth and development, physiology, and gene regulation in fungi. A. nidulans primarily reproduces by forming millions of asexual spores known as conidia. The asexual life cycle of A. nidulans can be simply divided into growth and asexual development (conidiation). After a certain period of vegetative growth, some vegetative cells (hyphae) develop into specialized asexual structures called conidiophores. Each A. nidulans conidiophore is composed of a foot cell, stalk, vesicle, metulae, phialides, and 12,000 conidia. This vegetative-to-developmental transition requires the activity of various regulators including FLB proteins, BrlA, and AbaA. Asymmetric repetitive mitotic cell division of phialides results in the formation of immature conidia. Subsequent conidial maturation requires multiple regulators such as WetA, VosA, and VelB. Matured conidia maintain cellular integrity and long-term viability against various stresses and desiccation. Under appropriate conditions, the resting conidia germinate and form new colonies, and this process is governed by a myriad of regulators, such as CreA and SocA. To date, a plethora of regulators for each asexual developmental stage have been identified and investigated. This review summarizes our current understanding of the regulators of conidial formation, maturation, dormancy, and germination in A. nidulans.
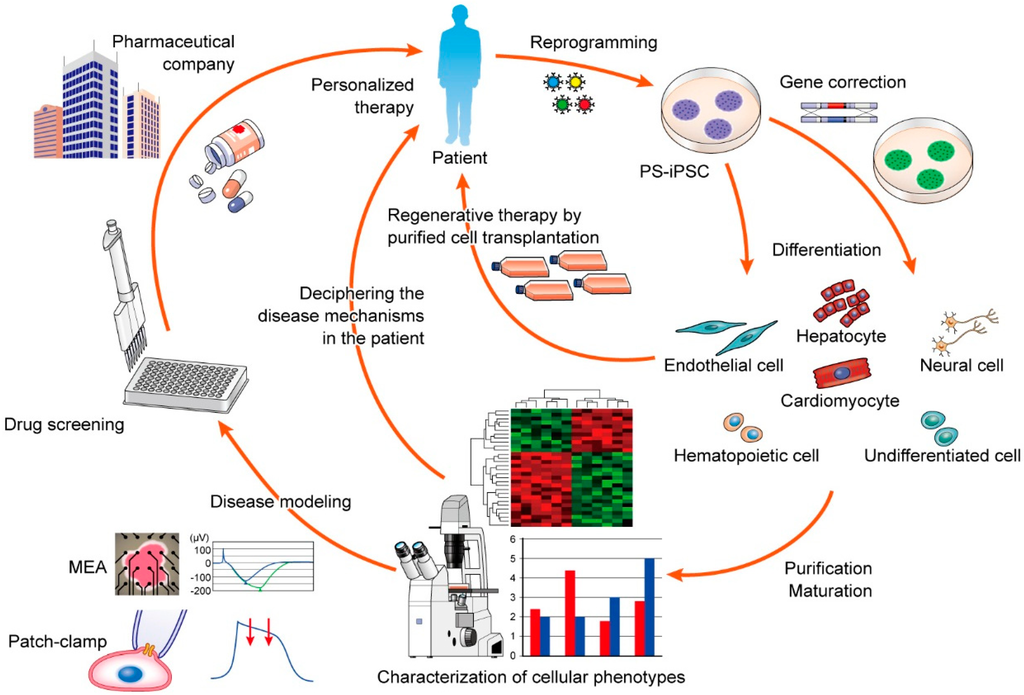
IJMS, Free Full-Text
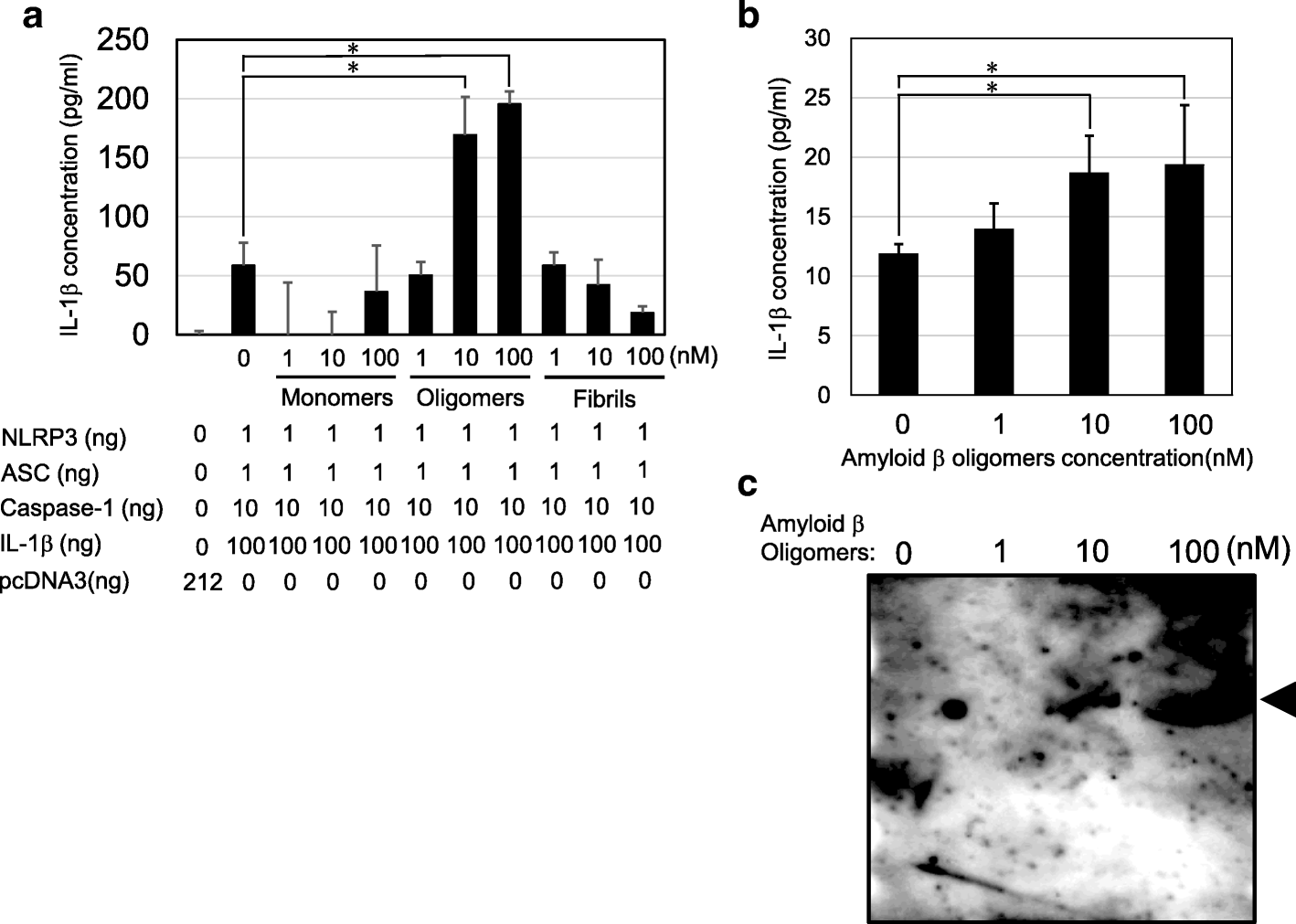
Amyloid β directly interacts with NLRP3 to initiate inflammasome activation: identification of an intrinsic NLRP3 ligand in a cell-free system, Inflammation and Regeneration
Oreilly Essential System Administration 3Rd Edition Aug 2002 Rar - Colaboratory

Cell-free expression and synthesis of viruses and bacteriophages: applications to medicine and nanotechnology - ScienceDirect
Ds Kumar Strömungsmechanik Pdf Kostenloser Download - Colaboratory
Cells, Free Full-Text
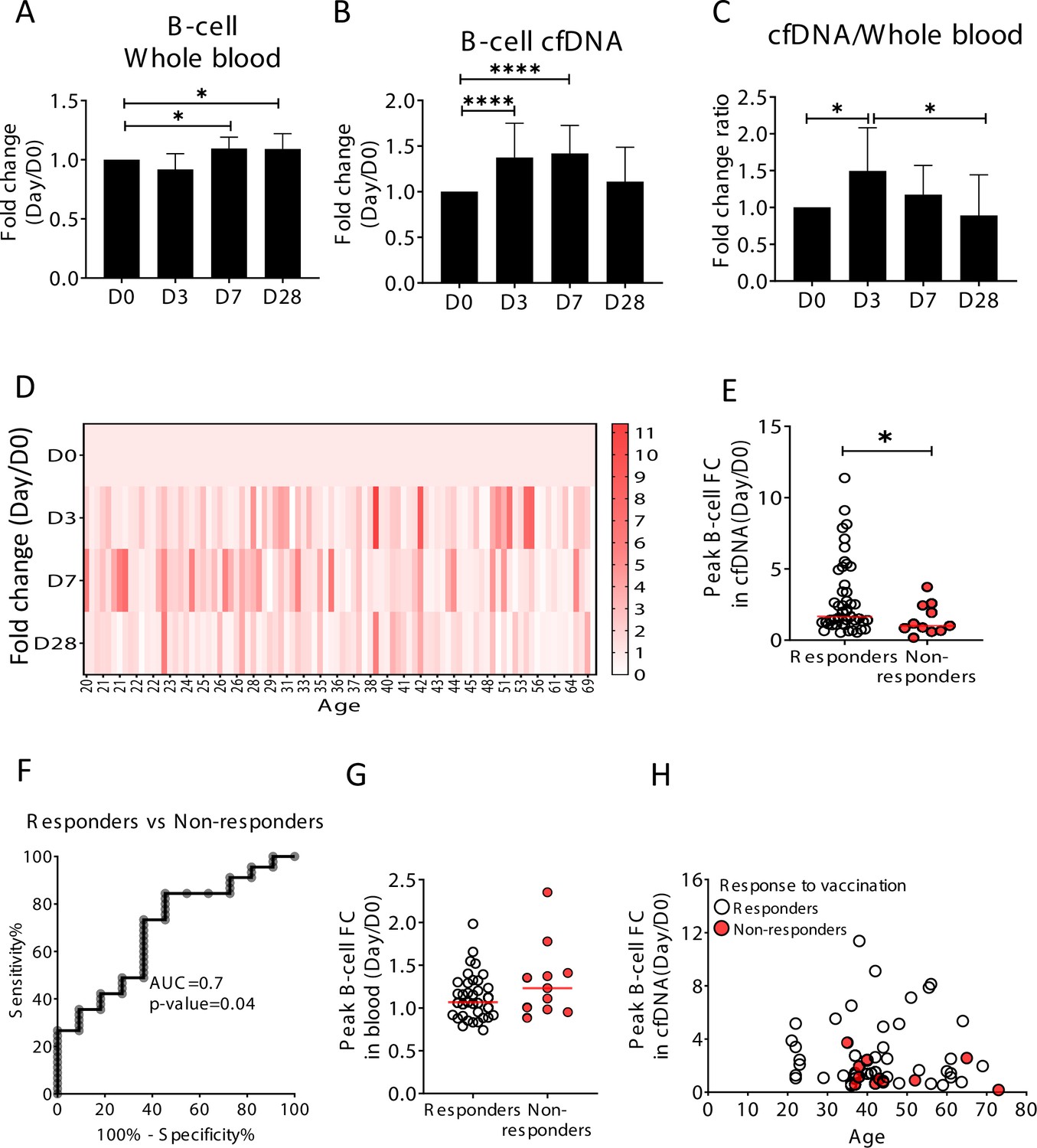
Remote immune processes revealed by immune-derived circulating cell-free DNA

The emerging impact of cell-free chemical biosynthesis - ScienceDirect

Effect of calendar ageing on the cycle life of anode-free full-cells.

An illustration of the full-duplex cell-free massive MIMO system.

Cell-Free DNA and Apoptosis: How Dead Cells Inform About the Living - ScienceDirect

Cell-free Macromolecular Synthesis

Cell-free DNA tissues of origin by methylation profiling reveals significant cell, tissue, and organ-specific injury related to COVID-19 severity - ScienceDirect
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)






